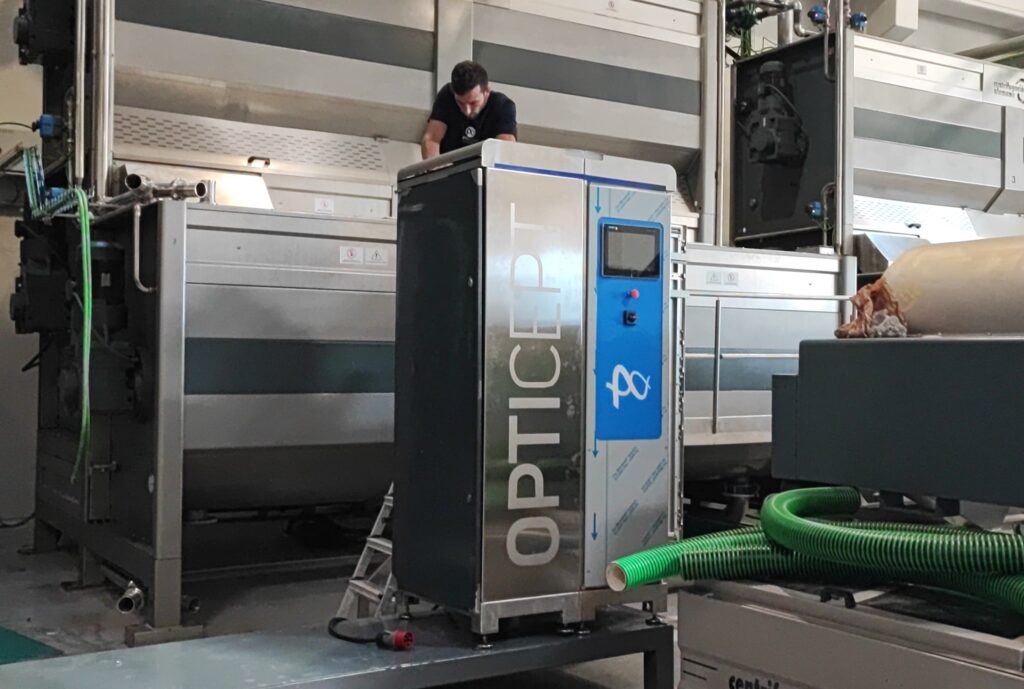
Juicier and softer pineapple slices – the effects of combining PEF and VI technologies
OptiCept has developed a new application area for the company’s technology platforms to improve product color and texture of pineapple chunks and other fruit and vegetable products as well.